طرخان
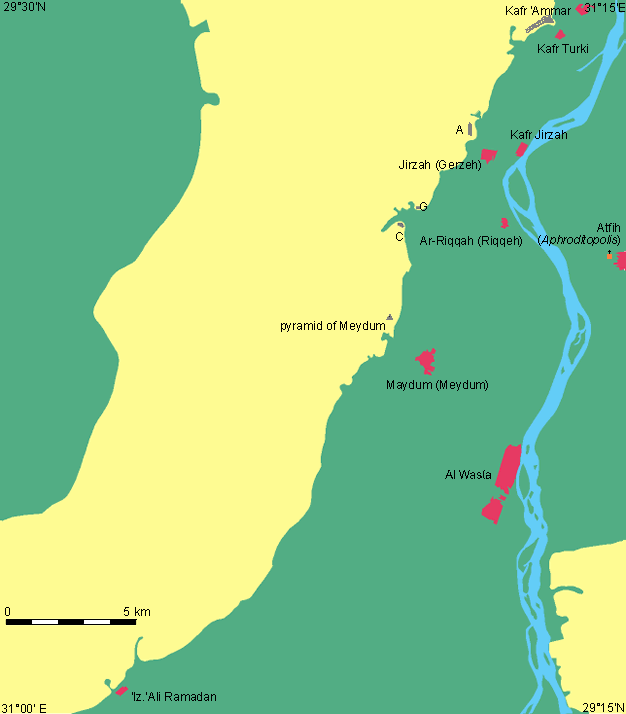
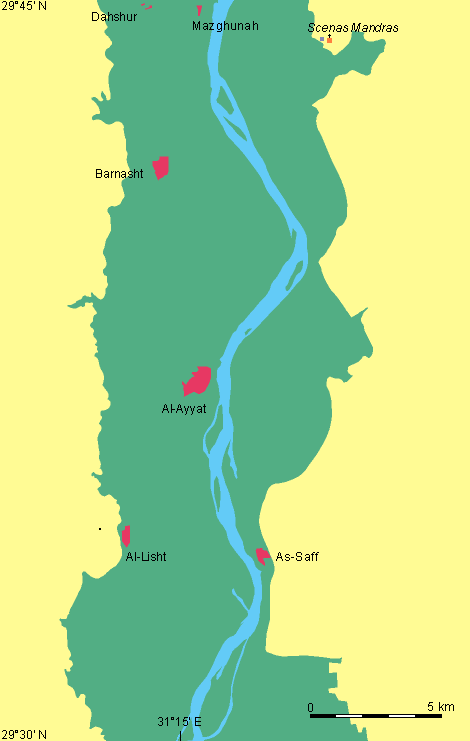
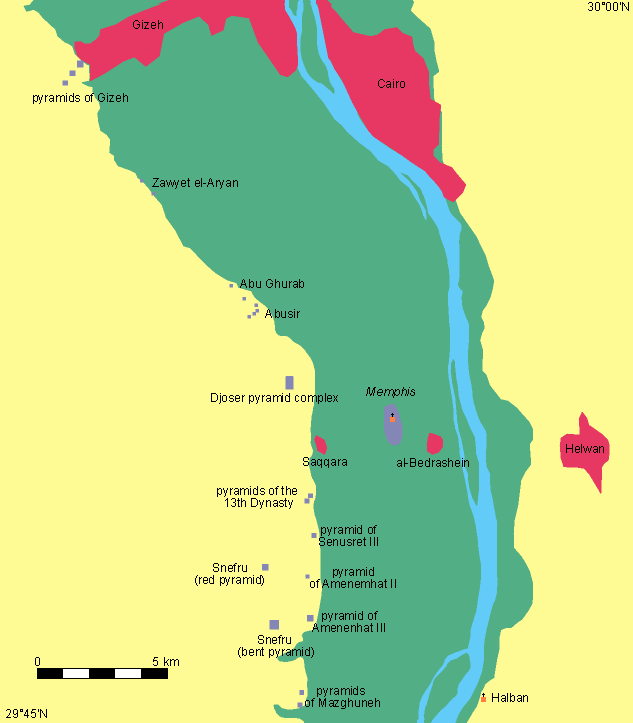
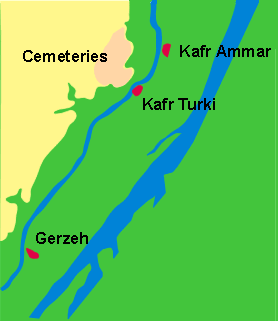
he site of a major cemetery dating from the Predynastic Period to the Roman Period south of Cairo on the west bank of the Nile near Kafr Ammar in the 21st nome of Upper Egypt. The bulk of the 2,000 tombs date to the foundation of the Egyptian
or Turkhan (Urdu: سلسله ترخان ) was established by Turkic Tarkhan and they ruled Sindh, Pakistan, from 1554 to 1591 AD. General Mirza Isa Beg founded the Tarkhan Dynasty in Sindh after the death of Shah Hassan Arghun of the Arghun Dynasty. Mughal …
Tarkhan-Mouravi — ( ka. თარხან მოურავი) (Tarkhnishvili, თარხნიშვილი, or Tarkhan Mouravishvili, თარხან მოურავიშვილი) is a Georgian noble family, claiming descent from the Shamkhal dynasty of Tarki, in Dagestan. Originally known as Saakadze (სააკაძე), they acquired …
Tarkhan (Egypt) — Tarkhan is the modern name for an Ancient Egyptian cemetery, located about 50 km south of Cairo on the West bank of the Nile.The cemetery was excavated in two seasons by Flinders Petrie. Tombs of almost all periods were found, but most…
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/House_of_Dadeshkeliani
The Dadeshkeliani or Dadishkeliani (Georgian: დადეშქელიანი, დადიშქელიანი) was an aristocratic family from the mountainous western Georgian province of Svaneti. They ruled the Principality of Svaneti from the 1720s to 1857.
History[edit]
Although the Dadeshkeliani themselves claimed the descent from the Shamkhal dynasty of Tarki, in Dagestan,[1] historic evidence shows that they were spun off from the House of Gelovani, a princely dynasty of Svaneti known since the 11th century.[2] One princess of the Gelovani family is said to have survived the destruction of her clan by the princes Dadiani, who usurped the Principality of Svaneti in the mid-17th century, and to have fled to Kabarda in the North Caucasus. Her eldest son, called Dadesh, married into a local princely family and his name was later transformed into a separate family name locally pronounced as Dadeshkeliani. His descendants were able to return to Svaneti to reclaim the domain from the Dadiani, attaining to the principate of Svaneti in the 1720s for the second time.Continuing dynastic strife among the Dadishkeliani, their defiance to the Russian government, and vacillation during the Crimean War (1854-1856), however, led to direct Russian intervention. In 1857, Prince Alexander Baryatinsky, Viceroy of the Caucasus, ordered Svaneti to be subdued by armed force. The prince of Svaneti, Constantine, chose to negotiate, but was ordered into exile to Erivan. On a farewell audience in Kutaisi, he quarreled with a local Russian administrator, Alexander Gagarin, and stabbed to death him and three of his staff. When captured, Constantine was summarily tried by court martial and shot. In 1858, the principality was abolished and converted into a district administered by a Russian-appointed officer (pristav). Several members of the Dadeshekeliani family were exiled to the remote Russian provinces and those who remained in Georgia were deprived of their privileges of autonomous princes.[3]